Role of Logistics in the Economy & A New Silk Road ( CPEC )
The scope and influence of logistics has evolved in the late 1940s. In the 1950s, and 60s, military was the only organization which used logistics. The scope of logistics has been extended beyond the army, as it has been recognized as one of the important tools for developing competitiveness.
Logistics facilitates in getting products and services as and when they are needed and desired to the customer. It also helps in economic transactions, serving as a major enabler of growth of trade and commerce in an economy.
The concept of logistics has its base upon the systems approach. There is a single chain, with flow of materials starting from the supplier, then to the plant and finally to the end customer, and also these activities are done sequentially in order to achieve customer satisfaction at low cost. For this to be successful there has to be co-ordination in the activities of the department.
Definitions;
American Council of Logistics Management: defines logistics as “the process of planning, implementing and controlling the efficient, cost effective flow and storage of raw materials, in-process inventory, finished goods and related information from point of origin to point of consumption for the purpose of conforming to customers’ requirements”.
Philip Kotler: defines logistics as “planning, implementing, and controlling the physical flows of materials and finished goods from point of origin to point of use to meet the customer’s need at a profit”.
The various functions of logistics are as follows:
1. Order Processing: Processing the orders received from the customers is an activity, which is very important by itself and also consumes a lot of time and paperwork. It involves steps like checking the order for any deviations in the agreed or negotiated terms, price, payment and delivery terms, checking if the materials is available in stock,producing and scheduling the material for shortages, and also giving acknowledgement to the owner, by indicating any deviations.
2. Inventory Planning and management: Planning the inventory can help an organization in maintaining an optimal level of inventory which will also help in satisfying the customer. Activities like inventory forecasting, engineering the order quantity, optimization the level of service, proper deployment of inventory etc. are involved in this.
3. Warehousing: This serves as the place where the finished goods are stored before they are sold to the customers finally. This is a major cost center and improper warehouse management will create a host of problems.
4. Transportation: Helps in physical movement of the goods to the customers place. This is done through various modes like rail, road, air, sea etc.
5. Packaging: A critical element in the physical distribution of the product, which also influences the efficiency of the logistical system.
Value delivery in the supply chain (Another Important Function )
The world has become a global village where due to liberalization and globalization, business organizations are forced to supply products beyond their national boundaries. Thus in such situations, the role of logistics is to provide time and place utility of the products to customers.
Also businesses are striving to attain competitiveness. In their struggle to survive, their focus has shifted to supply chain, and to deliver value for money for their customers. Logistics plays an important role in the process of delivering value and how successful the supply chain management is greatly depends on logistics planning and support.
Nowadays, the trend is to outsource. Organizations continue to outsource their operations because it is better to outsource the functional areas to experts who can do this job at a lower cost. This is one way of adding value.
Logistics from a Customs Perspective
For the first time in its history, the World Economic Forum’s Global Enabling Trade Report 2012 included questions on the “most problematic factors for exporting and importing” in its Executive Opinion Survey,the report stated: "This result underlines not only the importance of trade facilitation at multilateral and bilateral levels, but also the potential of countries for facilitating trade through practical measures within their government’s purview"
Improving Transport Infrastructure:
The Global Enabling Trade Report of the World Economic Forum emphasizes that there is immense potential for increasing global trade, and thereby economic growth, by reducing supply-chain barriers. The global transport and logistics sector will play a key role in releasing this potential. Rather than waiting for global growth to pick up, the global transport industry has already been forced to act, typically by enhancing efficiency, reducing costs wherever possible and investing in emerging markets. This can enable more efficient global trade of goods and stimulate economic development. But what else can be done? Can global trade be further stimulated by better logistics solutions? Fostering partnerships with countries is one way to achieve this.
Additive Manufacturing and Supply Chains:
Much has already been written about the effect of additive manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, on the future ability of consumers to manufacture their own devices at home. Most of the “home machines” spray thin layers of plastic resin one after another, until the layers add up to an object (hence the name “additive manufacturing”). The method, however, is also likely to replace significant portions of traditional industrial manufacturing.
Benefits and challenges for logistics:
With 3D printing, manufacturing complexity is no longer a constraint for hardware designers. The technique can be used to manufacture any shape, including complex hollow structures which are difficult to forge otherwise. Similarly, variety can be enhanced since the parameters of the computerized blueprint can be changed from item to item. This is likely to lead to a huge increase in consumers’ desire for customization.
Asian Logistics Industry
The robust trade, economic growth, and liberalization policies followed by many Asian countries have resulted in increased trade volumes. The ensuing increase in transportation, handling, and warehousing needs has led to a demand for integrated logistics solutions in the region.
In the case of India, the growing economy now requires a boost in its logistics services to keep the goods flowing at an increasing rate. The logistics field is now estimated at a value of more than $US14 billion, with further growth envisioned. Logistics-related services in India encompass transportation of goods by air, land, waterway, and railway.
China and Taiwan have been cooperating in efforts to improve logistics techniques. Since the advent of online shopping in China, the importance of delivery firms have grown manyfold. Taiwan's logistics centers are assisting Chinese logistics service providers nowadays. The huge potential of China's logistics scenario can be proved by the overall turnover in 2010, which was estimated at 110 trillion Chinese Yuan (US$16.6 trillion). This represents a huge business opportunity for logistics-related companies. The expected increase in China's GDP will give a further boost to this industry.
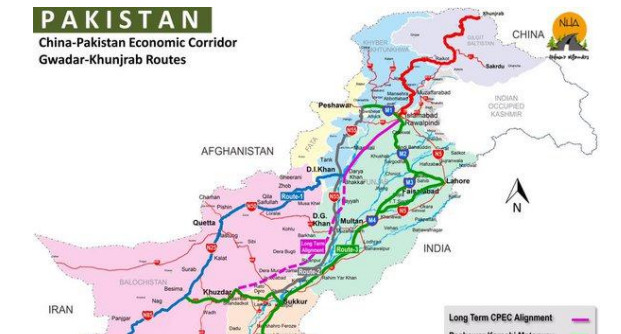
China Pakistan Economic Corridor ( A new Silk Road ):
The China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), the most debated development project in South Asia, will reportedly connect the region with Central Asia and Europe paving the way for rapid economic growth in the region.
China and Pakistan are the two major beneficiaries of the project. However all South Asian and Central Asian countries and Europe will have a good impact on their economies in the long run when the corridor will be fully operational for trade and logistics.
Besides Pakistan and China, other countries which will directly benefit from the CPEC are Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan and Afghanistan. These are landlocked countries and through the CPEC, they will get access to international waters for their indigenous products for trade including oil and gas while it will reduce the cost of restructuring of Afghan infrastructure.
The CPEC has been launched with the basic objectives of achieving economic integration through enhanced communication and increase in trade through building a corridor which would reduce the cost of logistics and transshipment time in the region.
Globally, the economic corridors are considered the most comprehensive form to connect countries for trade, industry and investment potentials with each other. In the long run, these corridors provide fast, efficient and reliable access to industrial production units and significant reduction in the transaction costs, including the logistics. This attracts the investors to invest in the region for increased profitability. These corridors are developed with the basic philosophy to connect different commercial, borders, and gateways and interchange points of a geographical locality for robust growth of the region. These types of corridors have been built in almost all parts of the world which have been benefitting the countries involved.
This is proved with European case where better connectivity led to better per capita income across Europe. The economic corridor operated in the Baltic States proved to be a good means for increasing exports and imports. Smaller states like Latvia and Estonia, which had experienced considerable economic turmoil in the aftermath of the breakup of Soviet Union, have now relatively high export-to-GDP ratios of 50 to 70 percent plus a complex export manufacturing base. These corridors have not only proven to be useful for economic growth between countries, but proved beneficial within a country too. The corridor between Jena and Berlin in Germany has helped the town of Jena regain its prominence in terms of being a world leader in optics.
It is therefore Pakistani and international experts see the CPEC as a game-changer for Pakistan.
The acceptance of China’s might has resulted in the huge Chinese investment in Pakistan, from development of Gwadar Deep Seaport to the CPEC and mega energy generation projections.
China was interested to take over this port because it opens up a route for transporting Middle Eastern oil by a 3,000km long land route from Gwadar port to Kashgar, the northwestern Chinese city – the least developed part of China as compared to others parts which is now the focus of Chinese government. China is both financing and constructing this most important seaport of Pakistan. Gwadar port is located just outside the Strait of Hormuz, which is the gateway for about 20 percent of the world’s oil.
Oil from the Middle East could be offloaded at Gwadar and transported to China by rail and road for which China requires a secure land route and the CPEC will provide this route.
Undoubtedly Pakistan has a golden opportunity to bank on the fact that the world’s second largest importer is in its neighbor and the country can truly regain its trade deficit by increasing its exports.
working as office Assistant
4ydear sir please suggest me an interesting topic for phd proposal which is some what relevant to finance.thanks